WTF is Finternet? Is it really different from the existing solutions?
Solana has recently launched a grant program of up to $10K per project for building Finternet using the Solana blockchain. Let's dive into Finternet and its use cases.
Moving towards decentralization with a pinch of centralization
With the evolution of web3, several new words were born including tokenomics, crypto-economics, tokenization, etc. A new term “Finternet” was introduced recently by Agustín Carstens, the general manager of the Bank for International Settlements, and Nandan Nilekani, Infosys Co-founder. But then wtf is Finternet?
Finternet= Financial + Internet
It means multiple financial ecosystems interconnected with each other, much like the internet, designed to empower individuals and businesses by placing them at the center of their financial lives.
Agustin and Nandan have recently published a paper, “Finternet: The Financial System for the Future”, explaining an interoperable financial system and the future of tokenization and unified ledgers. The paper is focused on multiple aspects of modern finance including interoperability, verifiability, programmability, immutability, finality, evolvability, modularity, scalability, security, and privacy.
Ahh! Too many “ity”s right?
But, this one definitely tells how tokenization is going to be the future. Let’s dive in.
According to BIS, the whole crypto ecosystem is flawed. They believe that with the help of blockchain technology, new digital tools need to be created to shape the modern financial system. This financial system will allow people to transfer money, buy stocks, or trade bonds instantly, without the need for complex intermediaries, lengthy verification processes, or any legal, regulatory, and institutional hurdles.
But how?
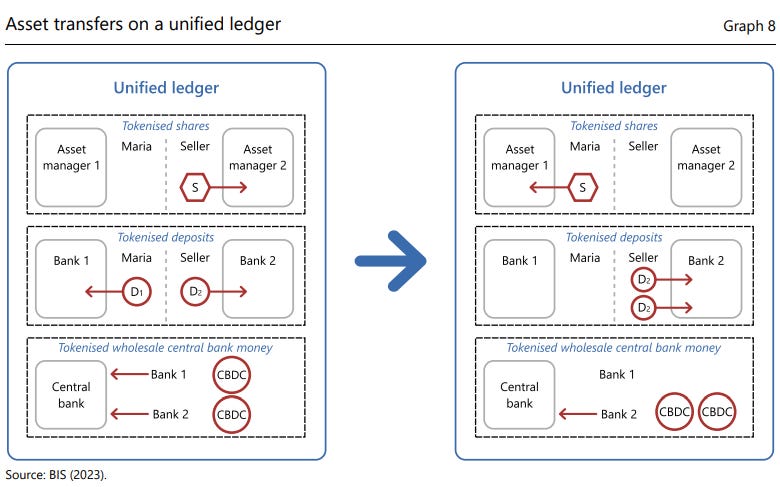
UNIFIED LEDGER
Unified ledgers are advanced digital platforms designed to consolidate multiple financial asset markets into a single, seamless system. These platforms enable the tokenization and execution of various assets, including:
Wholesale Tokenised Central Bank Money: Digital versions of central bank-issued currency for large-scale transactions.
Tokenised Commercial Bank Deposits: Digital representations of money held in commercial bank accounts.
Other Tokenised Assets: Digital forms of assets such as company shares, corporate or government bonds, and real estate.
It has been believed that with the unified ledger, financial transactions will be more efficient, fast, safe, and cheap, leaving enough space for new financial products to grow.
Why do we need Finternet?
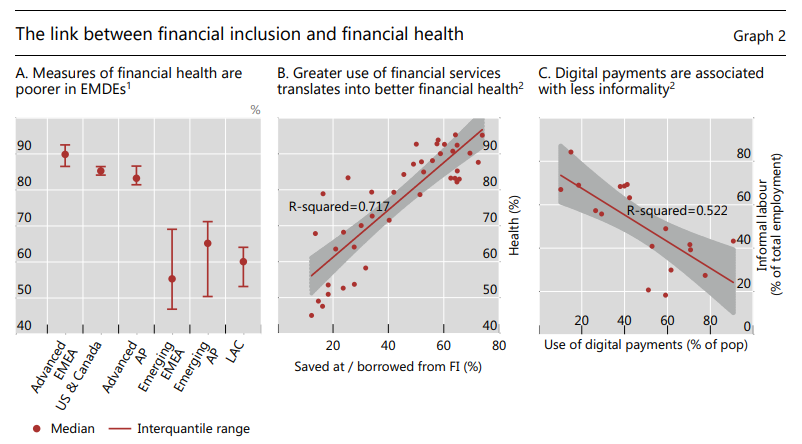
Current financial system: The current financial system has three main problems: it's slow, costly, and limited in access. Transactions often take days to process, with old systems causing delays. High costs arise from these slow processes, and a lack of competition makes financial services expensive. Many people, especially in emerging markets, struggle to access basic financial services or credit, which hampers their financial well-being and economic growth.
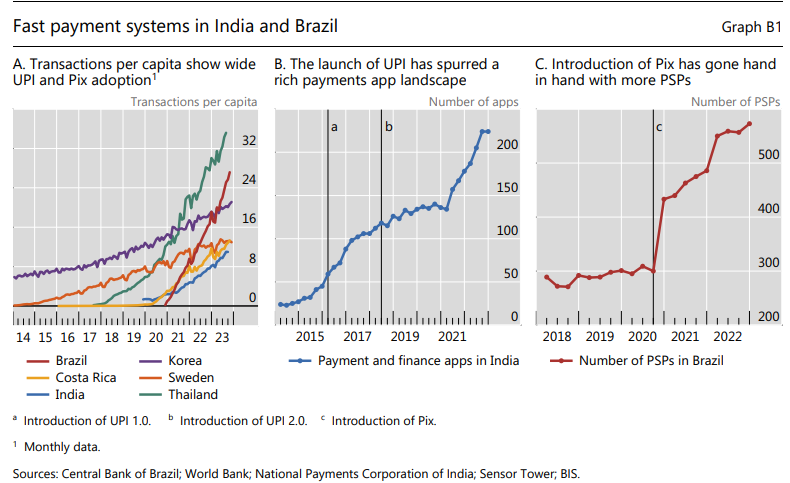
Technology-driven opportunities: Technological innovations like fast payment systems, digital identities, and tokenization are improving financial services by reducing costs, boosting inclusion, and speeding up transactions. Success stories like UPI in India and Pix in Brazil highlight the importance of private sector involvement alongside regulatory oversight. However, to fully realize the benefits, these advances need to operate within unified platforms supported by a strong governance framework.
The Finternet: The "Finternet" envisions a future financial system centered around user control, using advanced technologies and interoperability to simplify transactions. It aims to break down financial barriers, ensuring secure, fast, and accessible services, with regulatory oversight ensuring trust and innovation. Key lessons from India’s digital infrastructure show how this approach can drive inclusion and efficiency on a global scale.
What is Finternet?
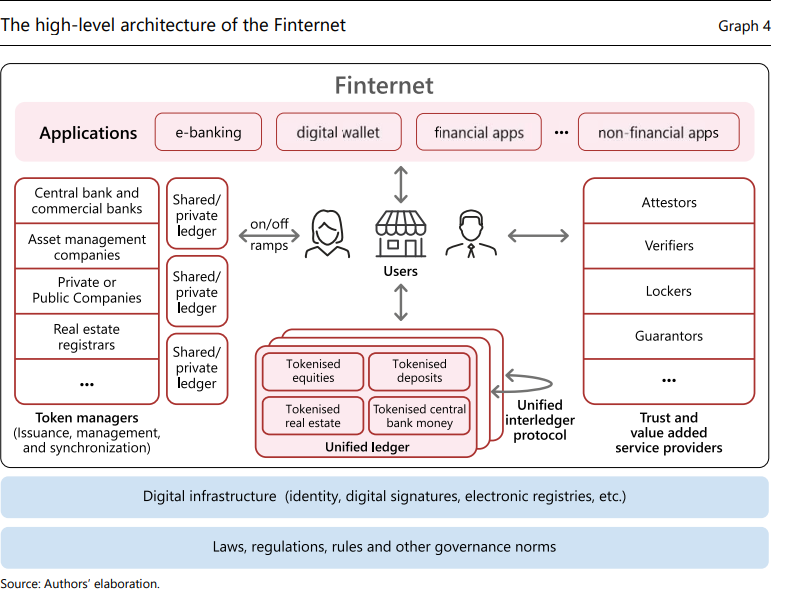
Finternet is a token-based financial system backed by unified ledgers.
These ledgers act as a shared platform where digital money and assets can seamlessly coexist, making transactions more efficient and secure.
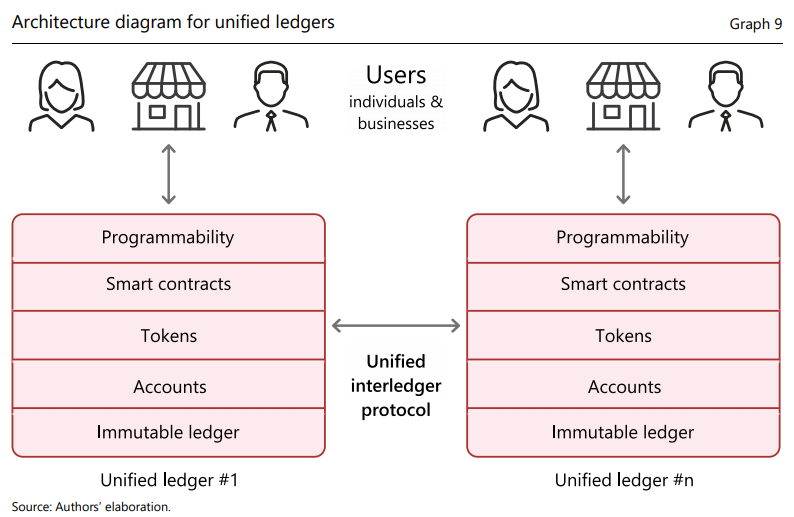
Unified ledgers won't centralize everything into one system; instead, they’ll allow different ledgers to connect via APIs, adapting to the needs of different jurisdictions.
This flexible, programmable structure opens up new possibilities for managing money and assets, automating processes with smart contracts, and eliminating reliance on external intermediaries.
At the core of this system is tokenized money, which serves as the unit of account and primary medium for transactions. Central bank and commercial bank money will continue to play their foundational roles, with central bank money offering settlement guarantees and tokenized commercial bank money facilitating retail transactions. As the system evolves, other tokenized assets—ranging from government bonds to real estate—could be added, depending on cost and benefit.
A unified ledger would simplify complex financial processes, like purchasing securities, by consolidating all necessary components into one place. For example, a stock purchase today involves multiple intermediaries and takes days to settle. Unified ledgers would streamline this, making such transactions faster and reducing points of failure. The system’s adaptability to different assets and jurisdictions makes it a promising path for the future of financial infrastructure.
Use Cases of Unified Ledgers and Tokenization
Investment: Unified ledgers allow fractional ownership of assets like bonds, making it easier for a person to invest with small savings.
Credit Access: Small businesses get loans cheaper and faster through automated, tokenised lending.
Insurance: Farmers use real-time data for adaptive, affordable insurance policies that mitigate farming risks.
Cross-Border Payments: Tokenised money speeds up remittances for workers, sending money home securely and efficiently.
Why Finternet important?
The Finternet is designed as a user-centric digital financial system, built on unified ledgers that ensure seamless, secure management of assets.
User-Centric Approach: The Finternet aims to offer universal access to financial services. Users can create accounts on different ledgers, manage multiple assets, and control their financial interactions in a flexible and secure way. Virtual addresses allow easy transactions across the system.
Interledger Protocol: A critical component of the Finternet, this protocol ensures that transactions across different ledgers are seamless and secure. It provides finality, meaning once a transaction is completed, it’s irreversible.
Trusted Identity and Data: The system requires verified digital identities for both individuals and businesses. Digital signatures and self-describing identities eliminate the need for repetitive identity checks (like KYC), streamlining access.
Tokenisation: Users can convert assets (e.g., real estate, stocks, or digital currencies) into digital tokens. These tokens are secure, carry data about their characteristics and rules, and can represent both tangible and intangible assets. The system ensures that transactions with these tokens are safe and complete.
Role of Token Managers: Entities like central banks or private companies act as token managers, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards. Users can manage their own tokens but cannot create tokens on behalf of others.
Smart Contracts: These automate transactions, adding trust and efficiency. They ensure that agreements are carried out without manual intervention.
Apps and Innovation: A diverse range of apps will enable users to manage all financial aspects, from investments to payments, using AI-driven insights. Businesses will benefit from real-time invoicing, financing options, and cross-border payments.
Security and Finality: Unified ledgers are secure and immutable, ensuring that once a transaction is recorded, it’s permanent. This immutability fosters trust and prevents fraud.
Different Token Types: Tokens can be fungible (like money) or non-fungible (like digital art). They can represent regulated assets (like stocks) or unregulated assets (like digital collectibles). Some tokens require identity verification, while others, like bearer tokens, allow for anonymous ownership.
The Finternet offers a powerful way to handle digital financial agreements using smart contracts—automated programs that execute agreements without human intervention. These contracts remove the need for middlemen and drastically reduce errors or delays. They can manage everything from simple money transfers to more complex financial deals.
What makes these contracts stand out is their flexibility. They can be deployed either remotely or directly on the Finternet’s unified ledger, making them versatile for a variety of tasks. This automation improves transaction speed, security, and accuracy, ensuring that agreements happen exactly as planned.
The system also supports a full infrastructure to help developers create and customize smart contracts. This includes:
Contract templates for common agreements
Policy frameworks to ensure contracts follow the law
Applets that allow contracts to interact with outside data or services (like real-world events)
The Finternet’s unified ledger meticulously tracks all data related to transactions, ownership, tokens, and more. In terms of fraud prevention, the Finternet tackles issues like identity theft, circumvention of rules, and internal threats with robust mechanisms:
At Entry: It uses advanced identity verification tools (biometrics, digital signatures) to prevent unauthorized access.
Within the System: Once inside, automated monitoring catches unusual activities, and the ledger's immutability prevents fraud, ensuring that any attempted alteration is easily traceable.
By embedding compliance rules into the system’s code (e.g., KYC and AML requirements), the Finternet ensures users meet all necessary regulatory criteria, safeguarding the integrity of the system from fraud and abuse.
Tech is evolving and making the system robust
Advances in cryptographic technologies, like encryption and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), have strengthened the security of digital financial systems by protecting data and ensuring transaction integrity. Digital signatures and verifiable credentials add an extra layer of trust, preventing tampering and establishing non-repudiation. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK proofs) stand out as a critical development, enabling parties to validate statements without revealing sensitive data. This innovation enhances privacy and confidentiality, which is key for secure identity verification and data sharing, helping drive a transformative shift in digital interactions.
Finternet and Regulation
For the Finternet to succeed, clear legal and regulatory frameworks are crucial. Existing laws should apply to new digital financial technologies, avoiding regulatory loopholes. Central banks’ authority to issue tokenized money must be clarified, as well as the legal status and tax treatment of tokenized assets. Jurisdictions might use this opportunity to introduce new norms, but governance issues, like ledger ownership and control, need careful consideration. International cooperation is vital for cross-border transactions to ensure seamless global financial integration.
What’s happening?
The Solana Foundation has earmarked up to $1M in grant funding specifically to fuel projects contributing to the realization of the "Finternet" on the Solana blockchain. At Global Fintech Fest, Nandan Nilekani and Siddharth Shetty presented a demo of money transfer on the Finternet using the Solana blockchain.
A project can earn up to $10K for building Finternet using Solana. More details: https://earn.superteam.fun/grants/finternet-grants/
The blockchain system is scattered and requires smooth integration and onboarding. Finternet, at its core, creates an interconnected, accessible, and efficient global financial ecosystem. The technology is not, but the representation is. While big names are showing interest in blockchain and tokenization, it would be interesting to see how new concepts with polished language will evolve. Will they shadow the current Web3 giants? Time will tell.
Follow me on X, LinkedIn and Medium.
References:
https://www.bis.org/publ/work1178.pdf
https://yourstory.com/2024/04/what-is-finternet-nandan-nilekani-interoperable-financial-ecosystem
https://community.nasscom.in/communities/digital-transformation/what-finternet-now
https://www.livemint.com/news/the-finternet-will-be-here-soon-are-you-ready-11713817836417.html
https://www.regulationasia.com/bis-outlines-vision-for-future-financial-system-called-finternet/



good read